2010 Toyota Yaris Detailed Finite Element Model
Version 2j, released Download Yaris zip 40.2 MB →
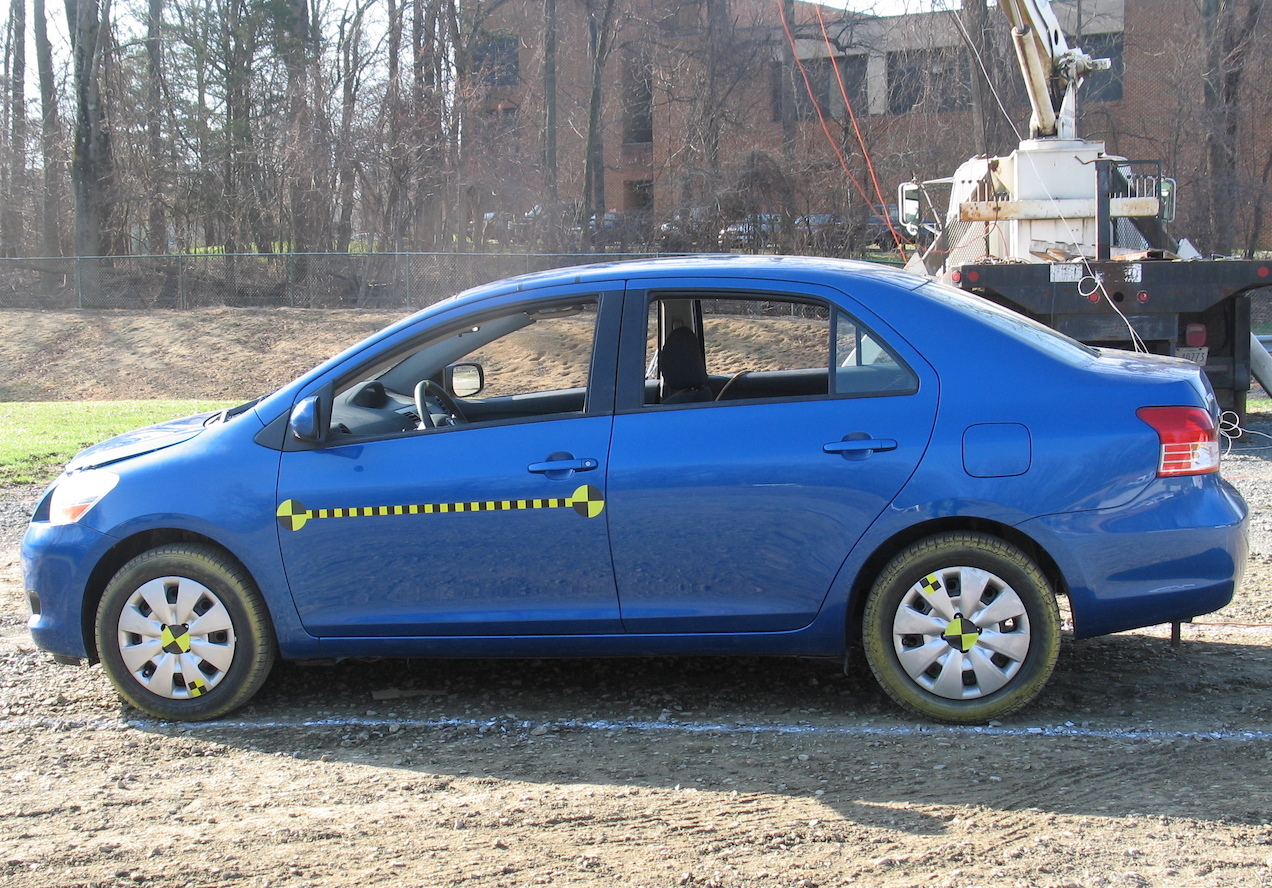

Vehicle Description
| VIN | JTDBT4K37 |
|---|---|
| Body Type | Sedan 4‐Door |
| Weight | 1,078 kg (2,377 lb) |
| Engine Type | 1.5‐liter L4 DOHC 16V |
| Transmission | Manual |
| Tire Size | P185/60R15 |
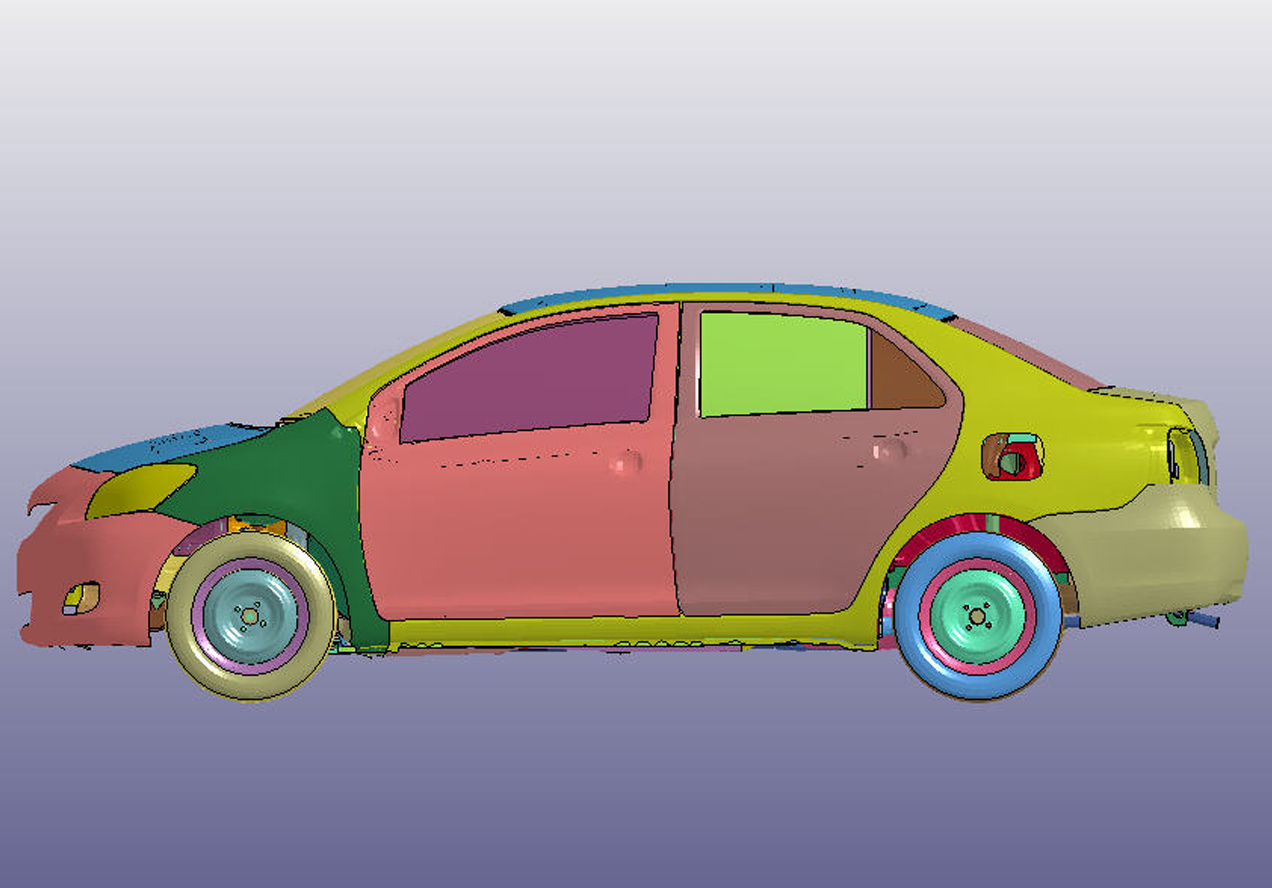
Version 2 Model Details
| Elements | 1,519,587 |
|---|---|
| Nodes | 1,488,581 |
| Parts | 940 |
| Features | Structural components details, Interior component details, Suspension system details, Uniform mesh throughout (multi mode impacts) |
References
- Development & Validation of a Finite Element Model for the 2010 Toyota Yaris Passenger Sedan, Tech Summary | NCAC 2011-T-001
- Extended Validation of the Finite Element Model for the 2010 Toyota Yaris Passenger Sedan, Tech Summary | NCAC 2012-W-005
- 2010 Toyota Yaris Finite Element Model Validation Detailed Mesh, Presentation | doi:10.13021/G8CC7G
This model is computer representation of a 2010 Toyota Yaris sub-compact passenger sedan for use in crash simulations. It was developed through a reverse engineering process by Center for Collision Safety and Analysis researchers under a contract with the Federal Highway Administration.
The model was validated against several full‐scale crash tests. It is expected to support current and future research related to occupant risk and vehicle compatibility, as well as barrier crash evaluation, research, and development efforts. The model conforms to the Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware requirements for a 1100C test vehicle.
Initial verification and validation of the model included completeness checks, comparisons of actual and model inertial properties, suspension response tests, and comparisons to actual frontal crash test data. Subsequent efforts compared simulation results to other available crash tests.
The resulting detailed finite element vehicle model has over 1.5 million elements. It includes details of the structural, drivetrain, as well as the interior components allowing for integration of occupant (dummy) models in the simulations. The model was constructed to include full functional capabilities of the suspension and steering subsystems allowing for non‐level terrain analyses.
Average element size of the model is 6–8 mm with a minimum size of 4 mm. Typical simulation time step is 1.0 μs. The model was created for use with the LS-DYNA nonlinear explicit finite element code. Approximate computation time to run a 200 ms simulation using 16 cores is .
Related stories and links
- R. Reichert, C.K. Park, R.M. Morgan, “Development of Integrated Vehicle‐Occupant Model for Crashworthiness Safety Analysis,” NHTSA Report No. DOT HS 812 087,
2010 Toyota Yaris Coarse Finite Element Model
Version 1l, released Download Yaris zip 11.2 MB →

Vehicle Description
| VIN | JTDBT4K37 |
|---|---|
| Body Type | Sedan 4‐Door |
| Weight | 1,078 kg (2,377 lb) |
| Engine Type | 1.5‐liter L4 DOHC 16V |
| Transmission | Manual |
| Tire Size | P185/60R15 |

Version 1 Model Details
| Elements | 378,376 |
|---|---|
| Nodes | 393,165 |
| Parts | 919 |
| Features | Structural components details, Interior component details, Suspension system details, Uniform mesh throughout (multi mode impacts) |
References
- 2010 Toyota Yaris Finite Element Model Validation Coarse Mesh, Presentation | doi:10.13021/G8JS5D
- VERIFICATION & VALIDATION REPORT of MGS Barrier Impact with 1100C Vehicle Using Toyota Yaris Coarse FE Model, Report | doi:10.13021/G8NK6N
- VERIFICATION & VALIDATION REPORT of New Jersey Concrete Barrier Impact with 1100C Vehicle Using Toyota Yaris Coarse FE Model, Report | doi:10.13021/G8X31D
This model is computer representation of a 2010 Toyota Yaris sub-compact passenger sedan for use in crash simulations. It was developed through a reverse engineering process by Center for Collision Safety and Analysis researchers under a contract with the Federal Highway Administration.
The model was validated against full-frontal impact and was excercised against full‐scale New Jersey and and MGS barriers crash tests. It is expected to support current and future research related to occupant risk and vehicle compatibility, as well as barrier crash evaluation, research, and development efforts. The model conforms to the Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware requirements for a 1100C test vehicle.
Initial verification and validation of the model included completeness checks, comparisons of actual and model inertial properties, suspension response tests, and comparisons to actual frontal crash test data. Subsequent efforts compared simulation results to other available crash tests.
The resulting coarse finite element vehicle model has over 378 thousand elements. It includes details of the structural, drivetrain, as well as the interior components allowing for integration of occupant (dummy) models in the simulations. The model was constructed to include full functional capabilities of the suspension and steering subsystems allowing for non‐level terrain analyses.
Average element size of the model is 12–16 mm with a minimum size of 4 mm. Typical simulation time step is 1.0 μs. The model was created for use with the LS-DYNA nonlinear explicit finite element code. Approximate computation time to run a 200 ms simulation using 16 cores is .
→ SHA384(2010-toyota-yaris-detailed-v2j.zip)= f68913788cbe520709323f76214054f16bdbeeb2b7ddd6da
→ SHA384(2010-toyota-yaris-coarse-v1l.zip)= 4f2b837ba0c85c2ef123a75201ac341c5de6763fb2768b81
